
Internet of Things – IoT
The internet of things, or IoT, is a system of interrelated computing devices, mechanical and digital machines, objects, animals or people that are provided with unique identifiers (UIDs) and the ability to transfer data over a network without requiring human-to-human or human-to-computer interaction.
A thing in the internet of things can be a person with a heart monitor implant, a farm animal with a biochip transponder, an automobile that has built-in sensors to alert the driver when tire pressure is low or any other natural or man-made object that can be assigned an Internet Protocol (IP) address and is able to transfer data over a network.
I- What is the Internet of Things?
The Internet of Things, or IoT, refers to the billions of physical devices around the world that are now connected to the internet, all collecting and sharing data. Thanks to the arrival of super-cheap computer chips and the ubiquity of wireless networks, it's possible to turn anything, from something as small as a pill to something as big as an aeroplane, into a part of the IoT. Connecting up all these different objects and adding sensors to them adds a level of digital intelligence to devices that would be otherwise dumb, enabling them to communicate real-time data without involving a human being. The Internet of Things is making the fabric of the world around us more smarter and more responsive, merging the digital and physical universes.
II- How does Internet Of Things work?
An IoT ecosystem consists of web-enabled smart devices that use embedded systems, such as processors, sensors and communication hardware, to collect, send and act on data they acquire from their environments. IoT devices share the sensor data they collect by connecting to an IoT gateway or other edge device where data is either sent to the cloud to be analyzed or analyzed locally.
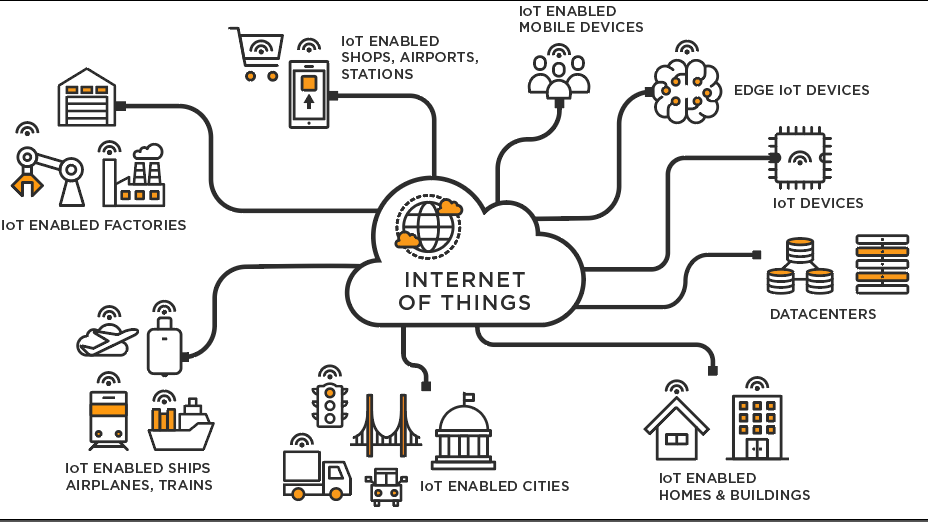
Sometimes, these devices communicate with other related devices and act on the information they get from one another. The devices do most of the work without human intervention, although people can interact with the devices -- for instance, to set them up, give them instructions or access the data.
The connectivity, networking and communication protocols used with these web-enabled devices largely depend on the specific IoT applications deployed.
IoT can also make use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to aid in making data collecting processes easier and more dynamic.
III- Why is Internet Of Things important?
The internet of things helps people live and work smarter, as well as gain complete control over their lives. In addition to offering smart devices to automate homes, IoT is essential to business. IoT provides businesses with a real-time look into how their systems really work, delivering insights into everything from the performance of machines to supply chain and logistics operations.
IoT enables companies to automate processes and reduce labor costs. It also cuts down on waste and improves service delivery, making it less expensive to manufacture and deliver goods, as well as offering transparency into customer transactions.
As such, IoT is one of the most important technologies of everyday life, and it will continue to pick up steam as more businesses realize the potential of connected devices to keep them competitive.
IV- What is an example of an Internet of Things device?
Pretty much any physical object can be transformed into an IoT device if it can be connected to the internet to be controlled or communicate information.
A lightbulb that can be switched on using a smartphone app is an IoT device, as is a motion sensor or a smart thermostat in your office or a connected streetlight. An IoT device could be as fluffy as a child's toy or as serious as a driverless truck. Some larger objects may themselves be filled with many smaller IoT components, such as a jet engine that's now filled with thousands of sensors collecting and transmitting data back to make sure it is operating efficiently. At an even bigger scale, smart cities projects are filling entire regions with sensors to help us understand and control the environment.
VI- Pros and cons of IoT
VI.1- Pros
Some of the advantages of IoT include the following:
- ability to access information from anywhere at any time on any device;
- improved communication between connected electronic devices;
- transferring data packets over a connected network saving time and money; and
- automating tasks helping to improve the quality of a business's services and reducing the need for human intervention.
VI.2 -Cons
Some disadvantages of IoT include the following:
- As the number of connected devices increases and more information is shared between devices, the potential that a hacker could steal confidential information also increases.
- Enterprises may eventually have to deal with massive numbers -- maybe even millions -- of IoT devices, and collecting and managing the data from all those devices will be challenging.
- If there's a bug in the system, it's likely that every connected device will become corrupted.
- Since there's no international standard of compatibility for IoT, it's difficult for devices from different manufacturers to communicate with each other.
Did you enjoy this blog? Please leave comments on what you think and contact us if you want to take our services 😊.

